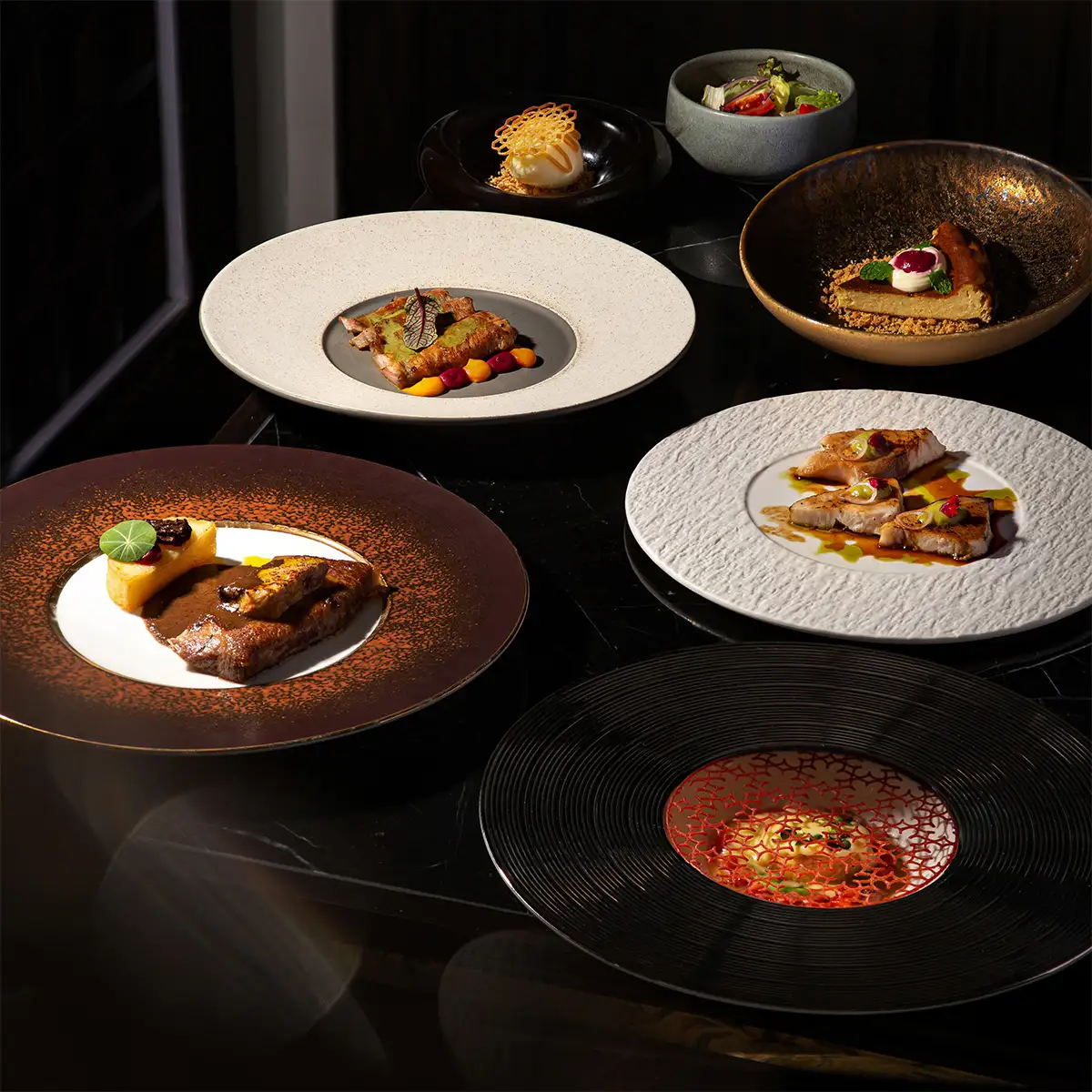
Michelin cooking techniques represent the pinnacle of culinary artistry, encompassing a range of advanced skills and methods employed by top chefs in the world's most prestigious restaurants. These techniques go far beyond basic cooking principles, requiring a deep understanding of food science, precision execution, and an unwavering commitment to excellence. This article aims to explore the key techniques that define Michelin-level cuisine, highlighting the complexity and precision involved in creating these exceptional dishes. Mastering these techniques is a challenging but rewarding pursuit for any aspiring chef seeking to elevate their culinary skills.
1. Mastering the fundamentals
While advanced Michelin cooking techniques often capture the spotlight, a solid foundation in fundamental skills is absolutely essential. These core competencies are the building blocks upon which all culinary masterpieces are created.
- Knife skills: Precise and consistent cuts are paramount in Michelin-level cuisine. Uniformity in size and shape ensures even cooking and enhances the visual appeal of the dish. Different knife techniques are employed for various ingredients, such as dicing (creating small cubes), mincing (finely chopping), and julienning (cutting into thin, matchstick-like strips). Maintaining knife sharpness is crucial for both efficiency and safety. A dull knife requires more force, increasing the risk of slips and injuries. Regular honing and sharpening are essential practices for any chef employing Michelin cooking techniques.
- Sauce making: Sauces are the soul of many Michelin-starred dishes, adding depth, complexity, and richness to the overall flavor profile. Mastering classic sauce techniques is fundamental. Reduction involves simmering a liquid to concentrate its flavor and thicken its consistency. Emulsification is the process of combining two immiscible liquids, such as oil and water, into a stable mixture. Hollandaise, béarnaise, and vinaigrettes are all examples of emulsified sauces. Creating complex and flavorful sauces from scratch requires a deep understanding of flavor pairings and the ability to balance acidity, sweetness, and umami.
- Stock preparation: A flavorful stock is the foundation of many sauces, soups, and braised dishes in Michelin-caliber cuisine. Stocks are made by simmering bones, vegetables, and herbs in water to extract their flavor. Different types of stocks are used for different applications, such as chicken stock for poultry dishes, beef stock for red meat dishes, and vegetable stock for vegetarian dishes. The importance of simmering and skimming cannot be overstated. Simmering gently extracts flavor without clouding the stock, while skimming removes impurities that can detract from its clarity and taste. Properly prepared stock is a hallmark of Michelin cooking techniques.
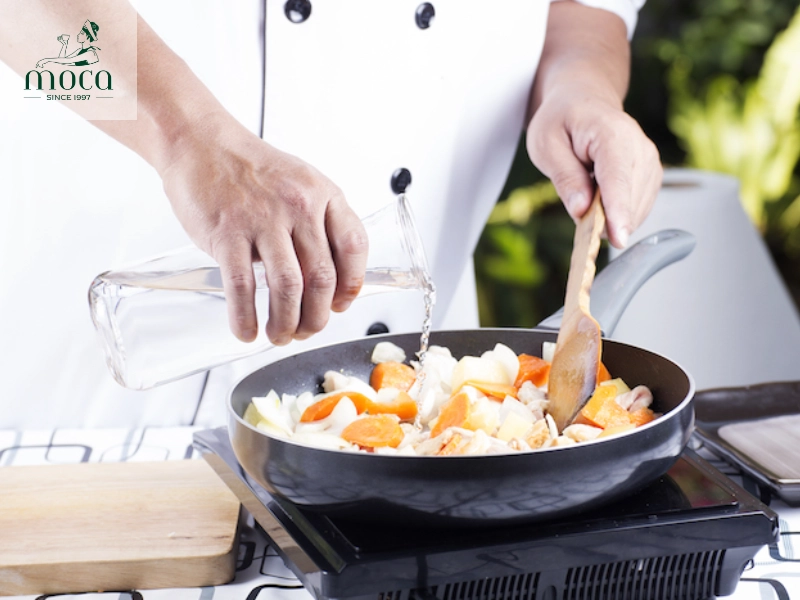

Behind every Michelin-level dish lies mastery of the basics. Precision, patience, and purpose—one technique at a time.
2. Advanced cooking techniques
Beyond the fundamentals, Michelin-starred chefs often employ a range of advanced cooking techniques to create innovative and visually stunning dishes. These techniques require specialized equipment and a deep understanding of food science.
- Sous vide: Sous vide, French for "under vacuum," is a technique that involves cooking food in a water bath at precise temperatures. The food is typically sealed in a vacuum-sealed bag, ensuring even cooking and maximum moisture retention. The benefits of sous vide are numerous, including precise temperature control, consistent results, and enhanced flavor. Examples of dishes prepared using sous vide include perfectly cooked steaks, tender chicken breasts, and silky-smooth custards. The precise temperature control afforded by sous vide is a hallmark of Michelin cooking techniques.
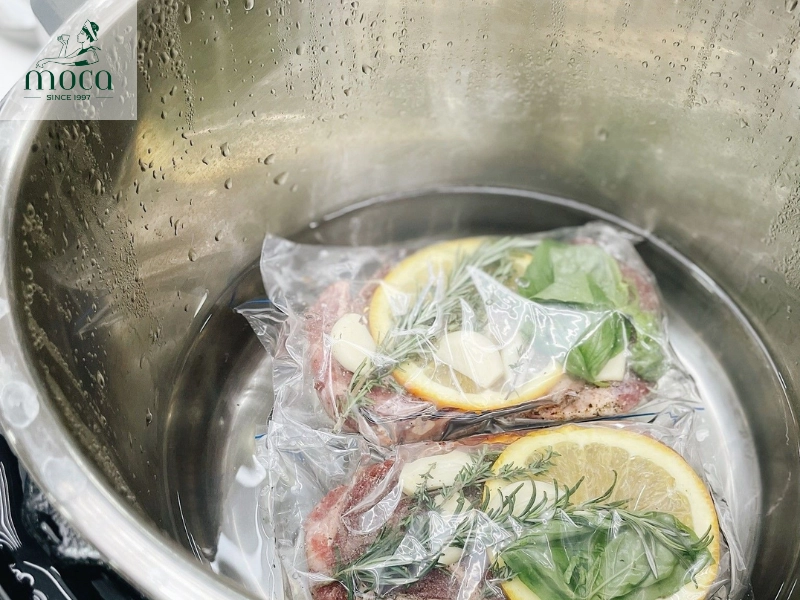

Sous vide delivers precision, tenderness, and unbeatable consistency—hallmarks of Michelin excellence.
- Spherification: Spherification is a molecular gastronomy technique that involves creating spheres of liquid with a thin, gel-like membrane. This is achieved by using sodium alginate and calcium chloride. The liquid is mixed with sodium alginate, then dropped into a calcium chloride bath, which causes the outer layer to gel, forming a sphere. Examples of spherified ingredients include caviar-like pearls of balsamic vinegar, fruit juice spheres, and even spherified cocktails. Spherification adds a playful and unexpected element to Michelin-starred dishes.
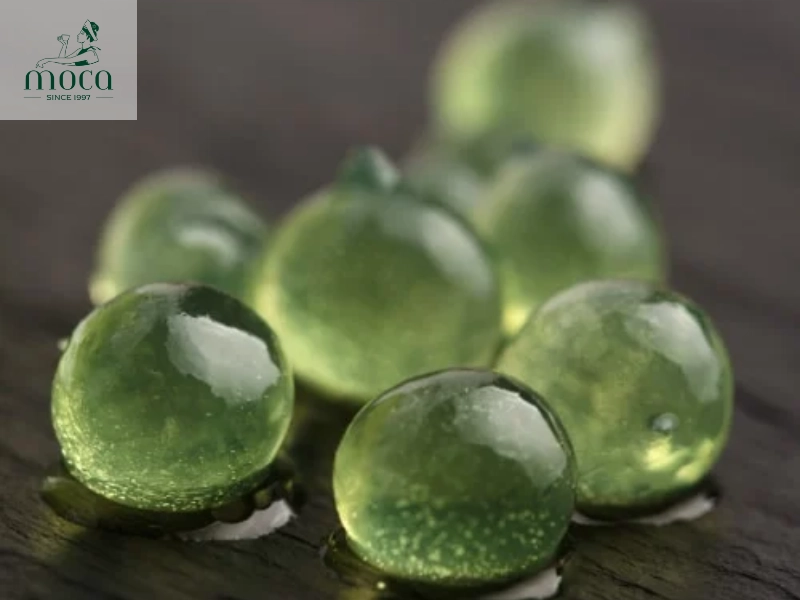

Molecular gastronomy meets elegance—liquid spheres that burst with flavor.
- Foams and airs: Foams and airs are techniques used to create light and airy textures that add visual appeal and enhance the flavor of a dish. These are typically created using a blender or immersion blender, often with the addition of lecithin as an emulsifier. Lecithin helps to stabilize the foam, preventing it from collapsing. Examples of foams and airs used in Michelin-starred dishes include citrus foams, herb airs, and even savory foams made from vegetables or broths.
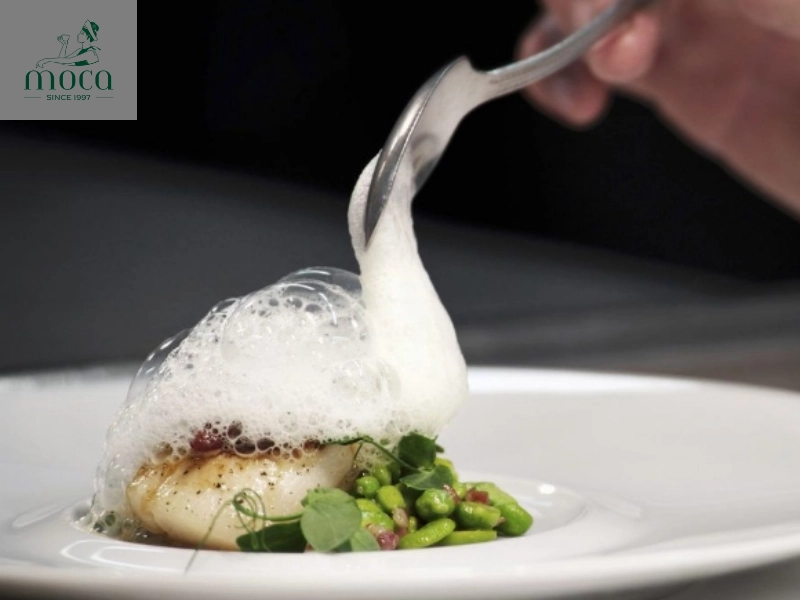

A whisper of flavor, a cloud of aroma—foams elevate taste and texture
- Gels and jellies: Gels and jellies are techniques that involve creating flavorful, semi-solid textures using gelling agents such as gelatin or agar-agar. Different types of gels can be created, including hot gels (which set when hot) and cold gels (which set when chilled). Gels and jellies are used in plating and presentation to add visual interest and create unexpected flavor combinations. Examples include fruit jellies, vegetable gels, and even savory aspics.
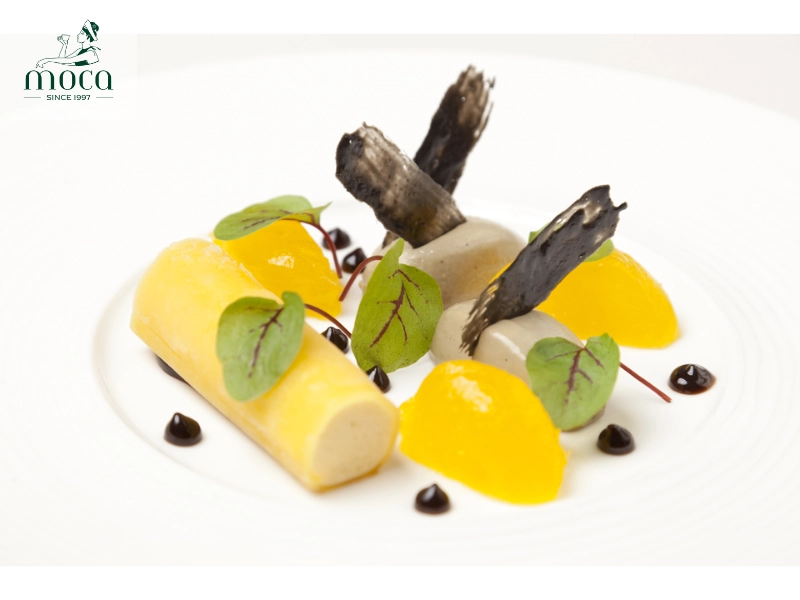

Form and function merge—jellies add both structure and surprise to the plate.
- Smoking: Smoking is a technique used to add smoky flavors to ingredients using a smoker or smoking gun. Different types of wood chips can be used to impart different flavors, such as hickory for a strong, smoky flavor, or applewood for a sweeter, more delicate flavor. Examples of smoked ingredients include fish, meat, vegetables, and even cheeses. Smoking adds depth and complexity to Michelin-starred dishes.
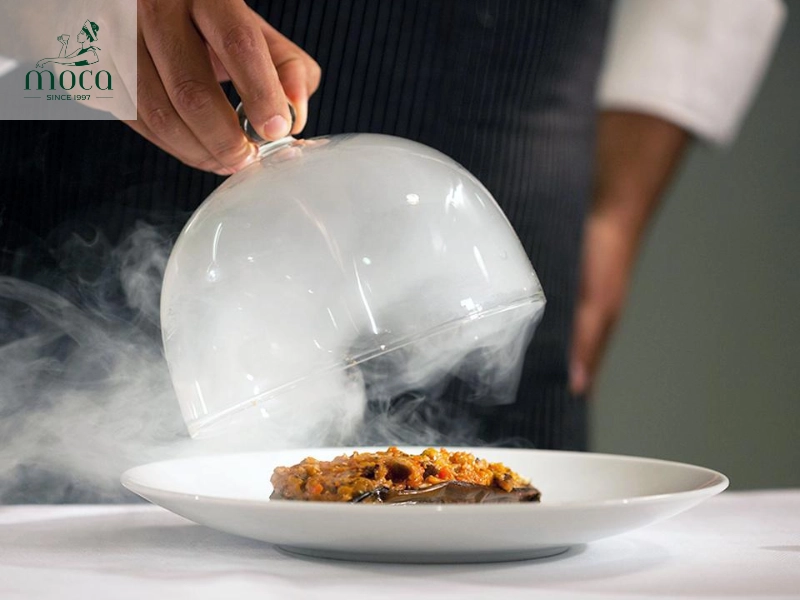

Flavor in the air—smoking ads mystery, aroma, and unforgettable depth.
Learn more: Exploring Vegetarian Michelin Restaurants
3. Precision and attention to detail
Beyond mastering fundamental and advanced cooking techniques, achieving Michelin-level cuisine requires an unwavering commitment to precision and meticulous attention to detail in every aspect of the cooking process.
- Temperature control: Precise temperature control is crucial for achieving desired results in many Michelin cooking techniques. Whether it's searing a steak to the perfect doneness or gently poaching an egg, accurate temperature control is essential. The importance of using thermometers and timers cannot be overstated. Thermometers ensure that food is cooked to the correct internal temperature, while timers prevent overcooking or undercooking. Sous vide, as discussed earlier, is a prime example of a technique that relies heavily on precise temperature control.
- Seasoning: Balancing flavors with precision is an art form in Michelin-starred kitchens. Seasoning is not simply about adding salt and pepper; it's about enhancing the natural flavors of the ingredients and creating a harmonious balance of sweet, sour, salty, bitter, and umami. Using different types of salt, pepper, and other seasonings can add complexity and depth to a dish. Seasoning at different stages of the cooking process is also important. For example, seasoning meat before searing helps to create a flavorful crust, while seasoning a sauce at the end allows for fine-tuning the flavor profile.
- Plating and presentation: In Michelin-level cuisine, the visual presentation of a dish is just as important as its taste. Creating visually stunning dishes requires careful consideration of plating techniques, color, texture, and composition. Different plating techniques, such as layering, stacking, and saucing, can be used to create a sense of depth and dimension. Paying attention to color and texture adds visual interest, while careful composition ensures that the dish is balanced and harmonious. The goal is to create a work of art that is both beautiful and delicious.
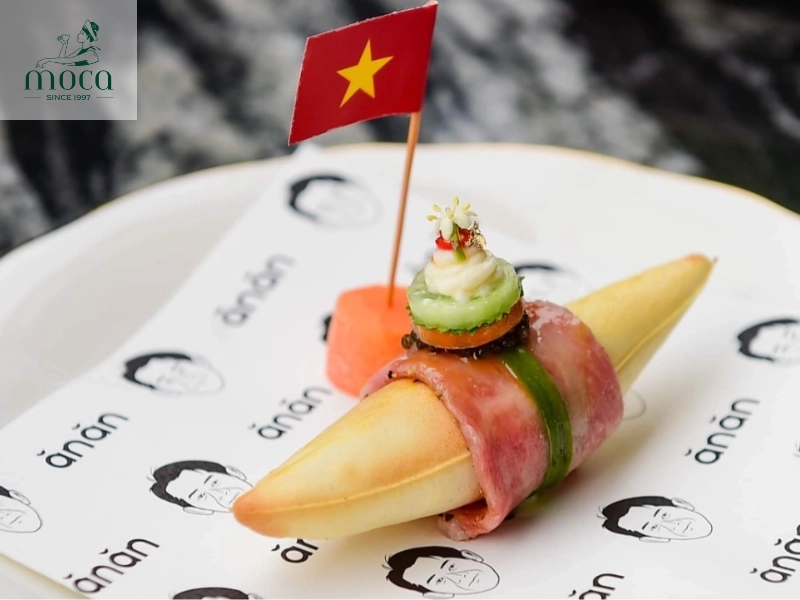

Every plate tells a story—plating is where taste meets visual poetry.
4. The importance of experimentation and innovation
While mastery of established Michelin cooking techniques is essential, the pursuit of culinary excellence demands a spirit of experimentation and a commitment to innovation. Michelin-starred chefs are constantly pushing culinary boundaries, seeking new ways to delight and surprise their diners.
- Pushing culinary boundaries: Experimenting with new techniques and ingredients is crucial for developing unique and innovative dishes. This might involve exploring new flavor combinations, incorporating unusual ingredients, or adapting traditional techniques to create something entirely new. Michelin-starred chefs are not afraid to take risks and challenge conventional wisdom in their pursuit of culinary innovation.
- Staying true to flavors: While innovation is important, it's equally important to balance it with a respect for traditional flavors. The goal is not simply to be different for the sake of being different, but to enhance the overall dish. Michelin cooking techniques should be used to elevate the natural flavors of the ingredients, not to mask or distort them. The best innovative dishes are those that are both surprising and familiar, offering a new perspective on classic flavors.
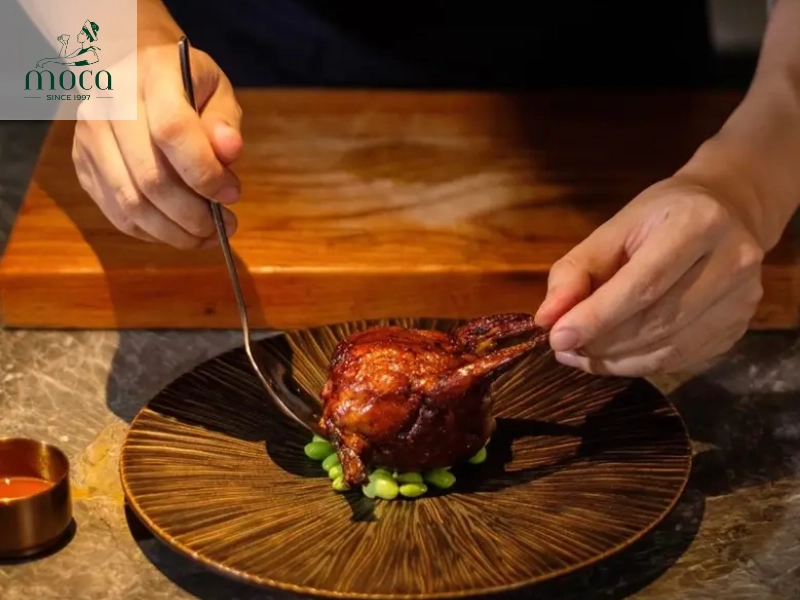

Michelin chefs push culinary boundaries, blending innovation with tradition to create unique, flavorful dishes.
Learn more: Gluten-free Michelin Restaurants In Ha Noi
In summary, Michelin cooking techniques encompass a wide range of skills, from mastering fundamental knife skills and sauce making to employing advanced methods like sous vide and spherification. Throughout, precision, meticulous attention to detail, and a commitment to innovation are paramount. We encourage aspiring chefs and culinary enthusiasts to explore these techniques, to experiment with new flavors and methods, and to appreciate the artistry and dedication that define the world of Michelin-starred cuisine.
If you're looking for more reviews on Michelin stars restaurants, don't hesitate to check out Moca Dining for more insights!
For reservations and more information, simply visit Moca Dining’s official website or contact us directly. We're here to make your dining experience truly memorable.
Contact details
Moca Dining
16 Nha Tho, Hang Trong Ward, Hoan Kiem District, Hanoi
Tel: 0819961997 | 08.1997.202